At the Israeli Hospitals Association (IHA), we specialize in supporting patients undergoing CAR-T cell therapy. Since 2019, we have dedicated ourselves to understanding every aspect of the CAR-T treatment journey, both medically and administratively. This comprehensive knowledge is invaluable for patients seeking CAR-T therapy in Israel, ensuring they receive the best possible care and guidance throughout their treatment process.
History of CAR-T therapy
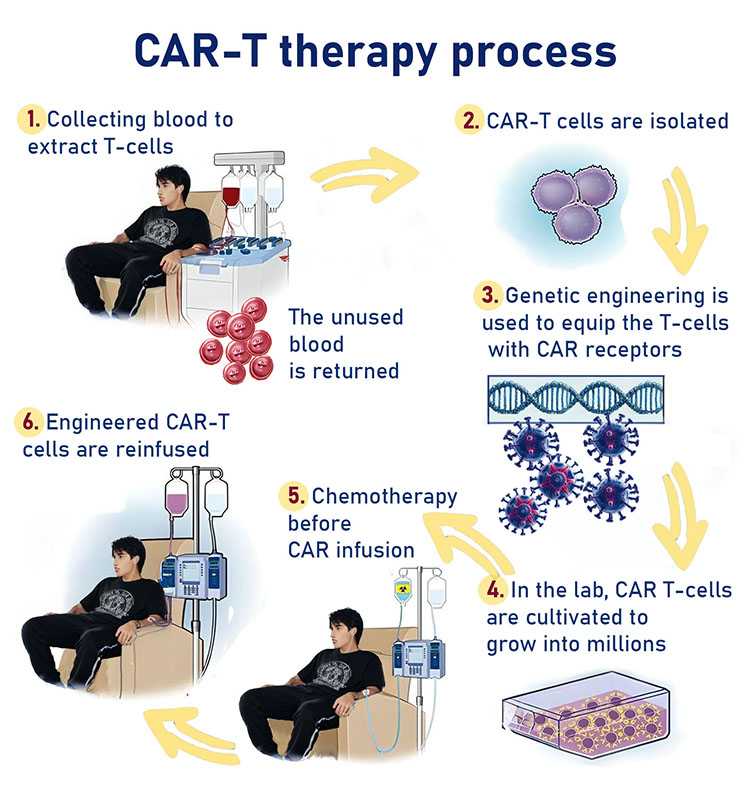
In 1987, Israeli scientist Zelig Eshhar, PhD, developed a novel type of engineered receptor called a "chimeric antigen receptor" (CAR), designed to treat cancer. This receptor is created by inserting DNA that encodes the CAR into T cells, enabling them to target and destroy cancer cells. The first clinical trial of CAR-T therapy took place in 2012 in the United States, with a young girl named Emily Whitehead as the recipient. Since that time, the FDA has approved six different CAR-T treatments for use in various types of cancer. As of 2023, Emily is doing well and has not experienced a recurrence of the disease.
CAR-T therapy in Israel 2024
Today, all major hospitals in Israel offer CAR-T therapy that has been approved by the FDA. However, the high cost of American-made CAR-T therapies, which can reach up to $500,000, has led Israeli hospitals to develop their own CAR-T treatments to make them more accessible to patients.
The prices of home-grown (in-house) CAR-T therapies are significantly lower.
Currently, a few hospitals in Israel provide the treatment. Among them, Sheba Hospital, Ichilov Hospital, and Hadassah Hospital offer their own in-house CAR-T therapies, approved by the Helsinki Committee and the Israeli Ministry of Health. The treatment is highly cost-effective. Contact us for detailed pricing information.
At this time, CAR-T therapy is used to treat certain types of blood cancer, including Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL), Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL), Leukemia (ALL) in children, Multiple Myeloma, and Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML).
Testimonial by a CAR-T patient at Hadassah hospital
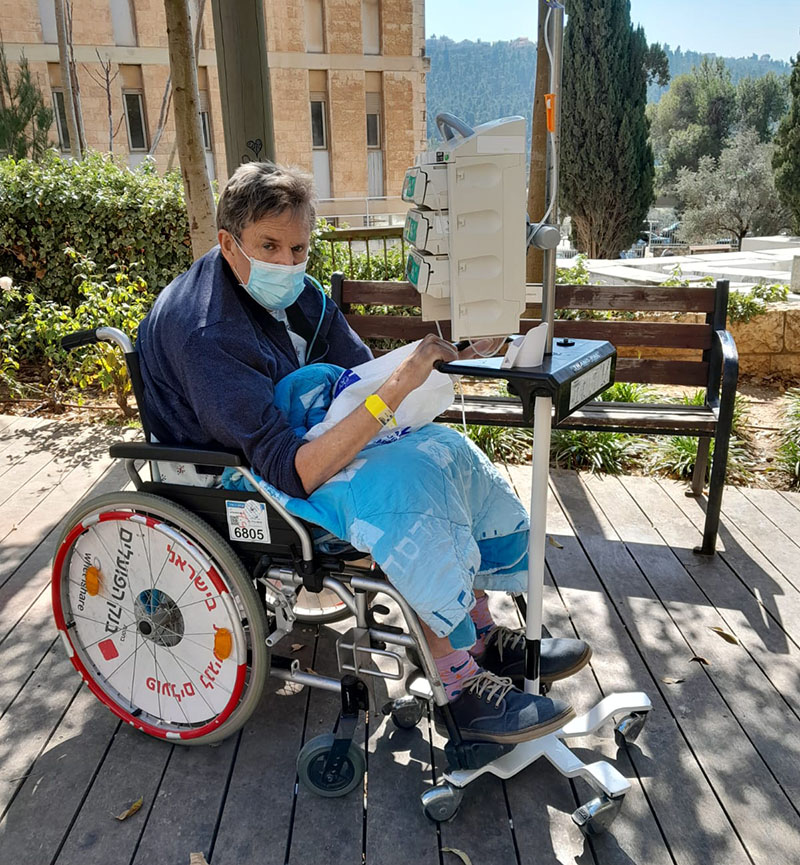

My Husband and I engaged with Tanya Preminger from IHA to travel from New Zealand to Israel for undertaking Car T treatment. During the preparation stage Tanya was very professional in her approach and extremely responsive to our many emails. During our 8 week stay in Israel Tanya was incredibly supportive on both a practical and social level. Tanya was an effective communicator with ourselves and the Hadassah hospital staff, always accountable and flexible with our needs. We would highly recommend Tanya as a representative for other clients who may be considering various treatments in Israel.
Yvonne and Mike Hogan, New Zealand, 8/5/2023

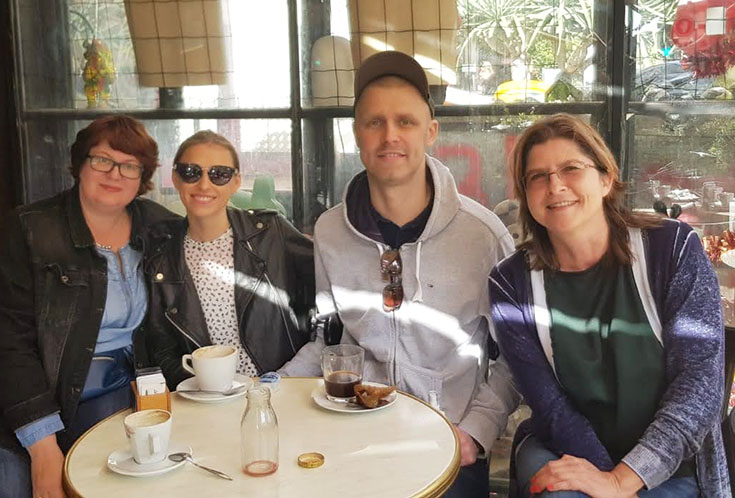
Enjoying coffee in Tel Aviv to celebrate a successful CAR-T therapy 2019.

Links
Initiating your CAR-T medical inquiry >>
CAR-T testimonials
CAR-T cell therapy in Sheba hospital in Israel
CAR-T cell therapy in Hadassah hospital in Israel










